poverty in malaysia article
Malaysia stated that its poverty figures was down to 04 in 2016 when compared to 49 in 1970. This shows that high level of poverty still exists in Malaysia and there is uneven income dis-tribution Economic Planning Unit 2015.

Making The Invisible Visible Faces Of Poverty In Malaysia
Such information is useful not only in understanding better the correlates and circumstances of poverty but also in identifying areas of government intervention for the redress of poverty.

. They point out that the income threshold used for the poverty linecurrently a monthly household income of 510 ringgit US134 in western peninsular Malaysiais. You are from the media he said. On the idea of weakly relative poverty see.
Table 3 showed that between these two regions a disparity was observed in the incident of poverty. Six in 10 households are unable to buy enough food for their families. And three eradicating poverty requires the active building of capacity confidence and non-financial capital among the poor rather than their just passively relying on cash transfers handouts or economic assistance.
Based on the official figures Malaysia is close to eliminating poverty and this is so for each of the three main ethnic groups. Compared to Sabah and Sarawak in Peninsular Malaysia IOP was lower to some extent. The Gros s Domestic Product PPP in Malaysia was reported at US1374093 in 2007 and US1473093 in.
In 2014 the Gini income coefficient of income inequality was at 041. With the recent revision of the National Mean Poverty Income Line PLI from RM980 to RM2208 more than 56 of Malaysians have fallen within this threshold. While rural poverty still continues to be the focus of policymakers urban poverty also needs urgent policy attention and prescriptions.
18128 Abstract Reports that urban poverty in Malaysia is not considered a serious phenomenon. However migration from rural areas to urban areas has increased urban poverty which has been exacerbated by crony capitalism and a rising cost of living. We believe that it can be tackled with the right.
This is followed by a summary of Income and Poverty Situation and Progress from between 1970 and 2014. Concepts like press freedom and conservation may not matter as much when one is poor and struggling to survive. The overall poverty rate is 37 in Malaysia Department of Statistics Malaysia 2011.
Is Malaysia Poor. I have proposed a new set of weakly relative poverty lines that yield a line for Malaysia that is at the level one would expect to find for a country at its level of economic development. The revised national poverty line income PLI which was reviewed in 2019 to ensure that the poverty measurements were in line with Malaysias socio-economic development saw the PLI increase from RM980 in 2016 to RM2208 in 2019.
This poverty level under MPI fell further to only 086 per cent of households nationwide in 2016. Welcomed by the World Bank upon following its announcement the PLI revision showcased Malaysias commitment to eradicating poverty. But the issue of child poverty the state of children living in poverty including children from poor families and.
Concurring with Ravallion Philip Aston the UNSR on Poverty and Human Rights in his report in August 2019 states that while Malaysia has achieved undeniably impressive growth in reducing poverty in the last 50 years the official claim that poverty has been eradicated or exists merely in small pockets in rural areas is incorrect and has crippled policymaking. Absolute poverty absolute hardcore poverty and the relative poverty. Poverty in Malaysia and reduced to 06 in 2014.
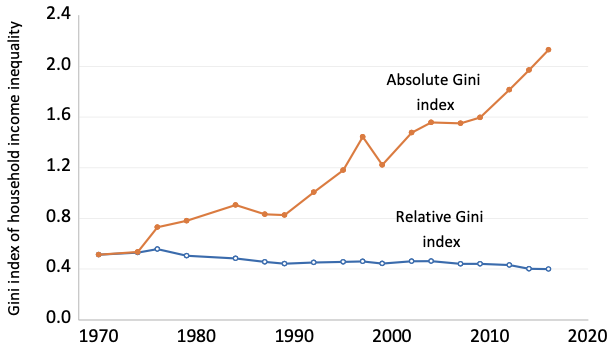
THE other day I was having my vegetarian lunch at a Chinese coffee shop and to my surprise when I finished there was an elderly uncle waiting for me on the pavement outside. Malaysia is no longer just grappling with absolute poverty but also with relative poverty pockets of persistent poverty and urban poverty as well as increasing inequalities. Malaysias household income inequality Gini coefficient declined from 0513 in 1970 to 0399 in 2016.
A profile of poverty in Malaysia is constructed which identifies the poor in terms of socioeconomic variables such as race location employment status occupation and education. We write this article to elaborate on three overarching strategies to resolve urban poverty in Malaysia. 2a gives the national poverty measuresThe compound growth rate in the poverty index is an impressive 99 per annum.
The definition of absolute poverty is when the households gross monthly income was not enough to support the minimum of basic need of life such as clothing health-care house rent and education. The current official poverty line is almost certainly too low by prevailing standards of what poverty means in a country such as Malaysia. In the aspect of ethnicity Bumiputera as the largest.
Even prior to the pandemic 25 of Malaysian adults were identified as food insecure ie lacking access to food primarily due to poverty. Based on the MPI benchmarks used by Malaysia the official findings in 2014 showed only 11 per cent of total households nationwide were multidimensionally poor or facing deprivations in multiple aspects of life. Next we discuss the need for a paradigm shift with respect to poverty given the new developments both in approaches and measurement.
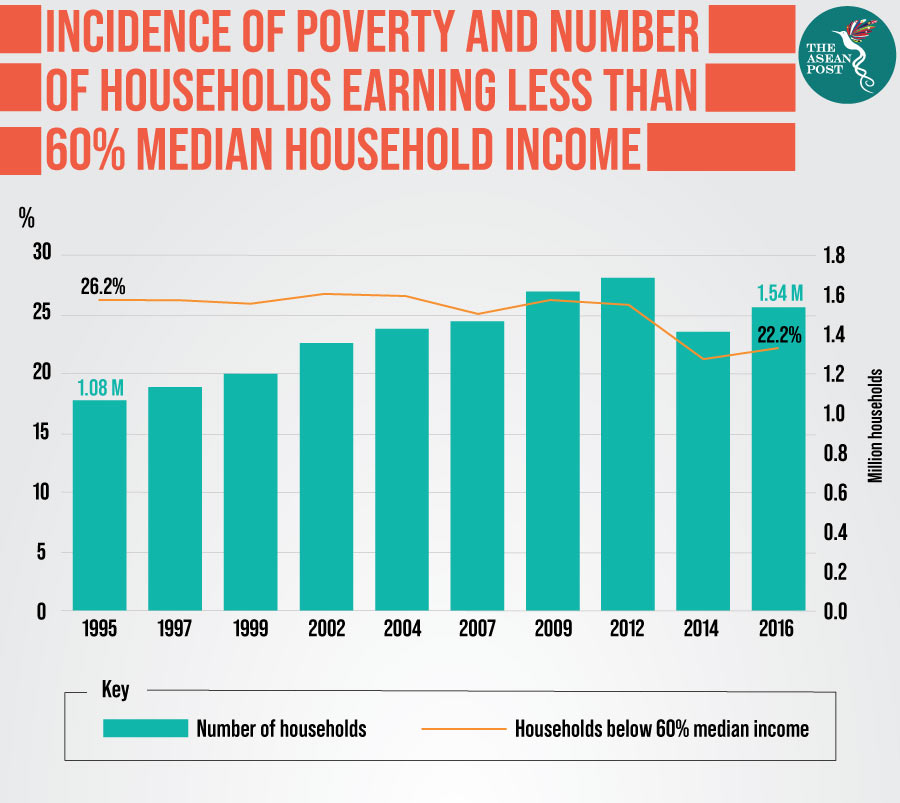
Reports often point to the fall in absolute poverty levels in Malaysiafrom 29 percent in 1980 to about 5-6 percent in 2000. In Malaysia there are three concepts of poverty that we are able to adopt. However the gap between the T20 the top 20 of households by income and the M40 the next 40 of households rose from RM6000 to RM10000 while the T20B40 gap rose from RM8000 to RM14000 from 1995 to 2016 before adjusting for inflation.
In 1976 it was reportedly at 583 and 565 respectively. The World Bank estimates that some 56 of Malaysian households are currently living in absolute poverty. That figure is now estimated to be 30 says Unicef.
This is because Malaysia defined poverty as household income per month less than RM 980. In 2020 some 22 of Malaysians reduced their meal sizes. The GDP per capita in Malaysia was last reported at US7760 in 2007 and US53645 in 2011.
Stubborn pockets of poverty continue to elude policy. The national poverty headcount which is the percentage of the population living below the poverty line was 06 percent in 2014 down from 6 percent in 2002. This paper begins with a brief review of major works on poverty in Malaysia.
But critical analysts complain that this figure is misleading. However UN officials argued that Malaysia has set the poverty line too low and household income more than RM 980 but less than RM 2000 are in fact under the poverty category also. 15 The NEPs target of bringing the official poverty rate down to 17 by 1990 was achieved.
However rapid urbanization and industrialization is expected to bring in rural migrants into urban centres bringing along low incomes while putting pressure on urban services infrastructure and the environment. In Malaysia the national mean poverty line income is RM2208 for households and RM1169 per household for the hardcore poor.

Malaysia Has Raised Its Poverty Line By More Than 100 Where Do Things Go From Here Cna

The Philippines Has The Most Persistent Poverty In South East Asia Southeast Asia Philippines Purchasing Power Parity
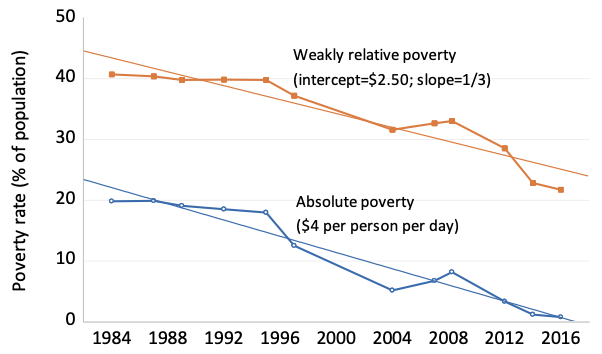
Ethnic Inequality And Poverty In Malaysia Since May 1969 Vox Cepr Policy Portal

5 Girls 1 Public Flat A Tale Of Hope Despair In Kuala Lumpur Poverty Children Poverty Girl
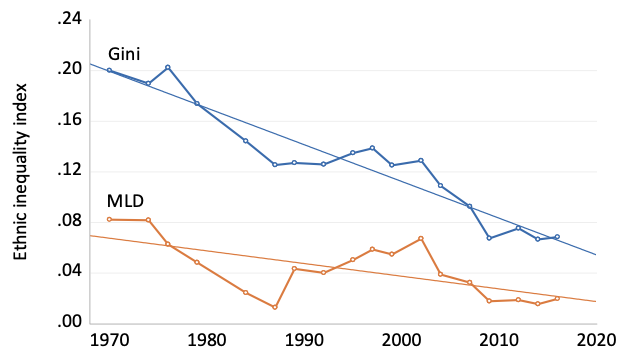
Ethnic Inequality And Poverty In Malaysia Since May 1969 Vox Cepr Policy Portal

Malaysia Poverty Rate Of Rural And Urban Areas 2019 Statista
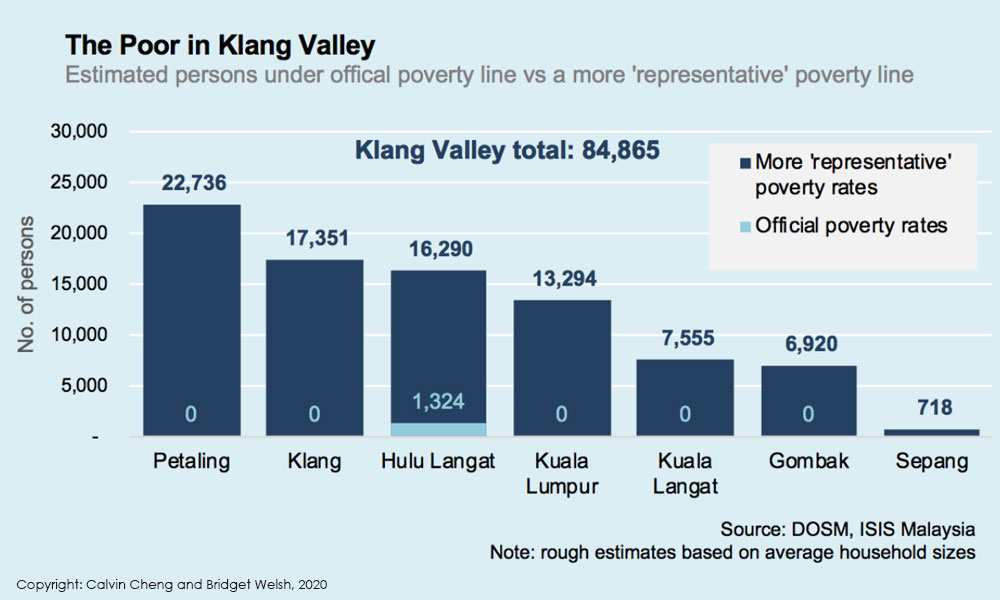
Making The Invisible Visible Faces Of Poverty In Malaysia

Poverty Becomes A Merciless Partner With Covid 19 In Malaysia
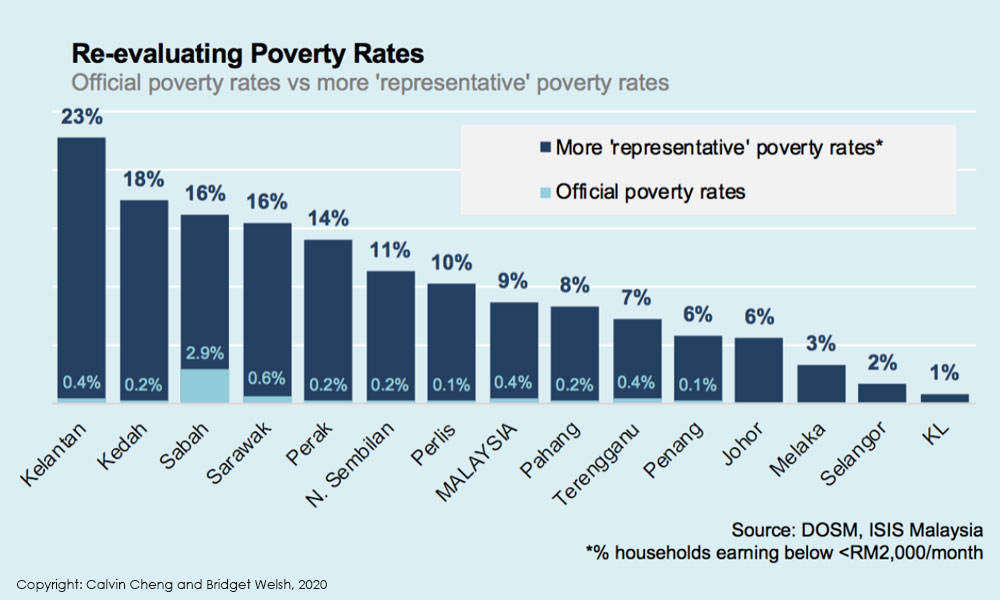
Making The Invisible Visible Faces Of Poverty In Malaysia

It Just Takes Rm900 A Month To Lift Urban Poor Out Of Absolute Poverty The Edge Markets

10 Facts About Poverty In Malaysia The Borgen Project
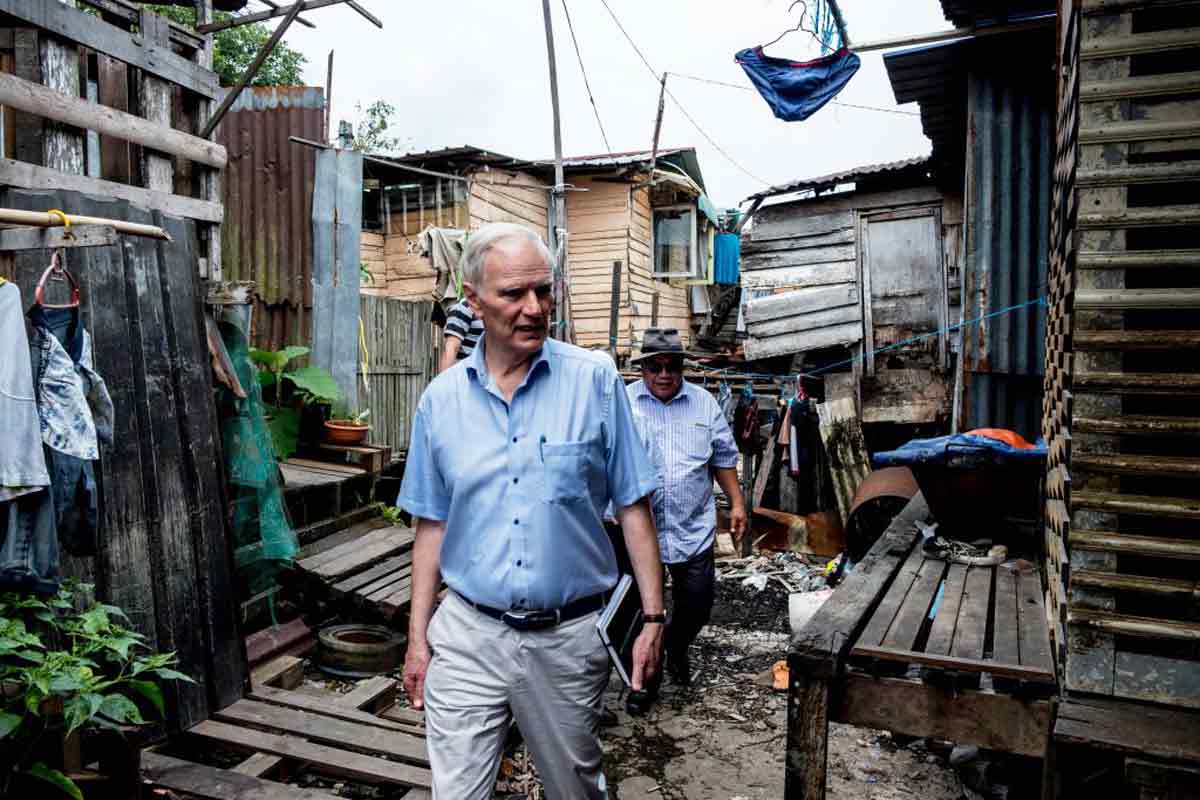

Malaysia World Champion For Conquering Poverty The Asean Post
Ethnic Inequality And Poverty In Malaysia Since May 1969 Vox Cepr Policy Portal
Malaysia World Champion For Conquering Poverty The Asean Post
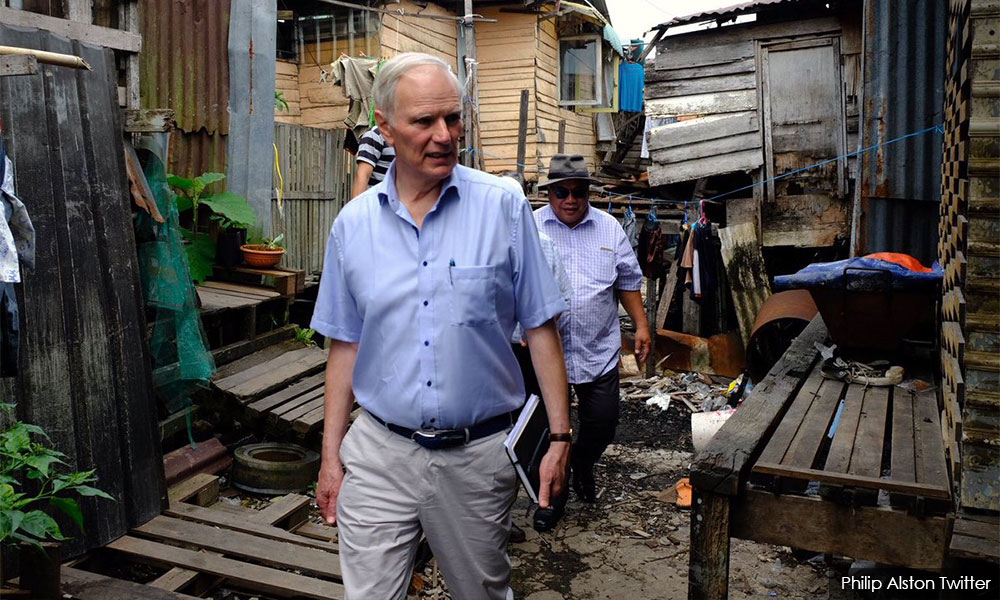

Making The Invisible Visible Faces Of Poverty In Malaysia

It Just Takes Rm900 A Month To Lift Urban Poor Out Of Absolute Poverty The Edge Markets
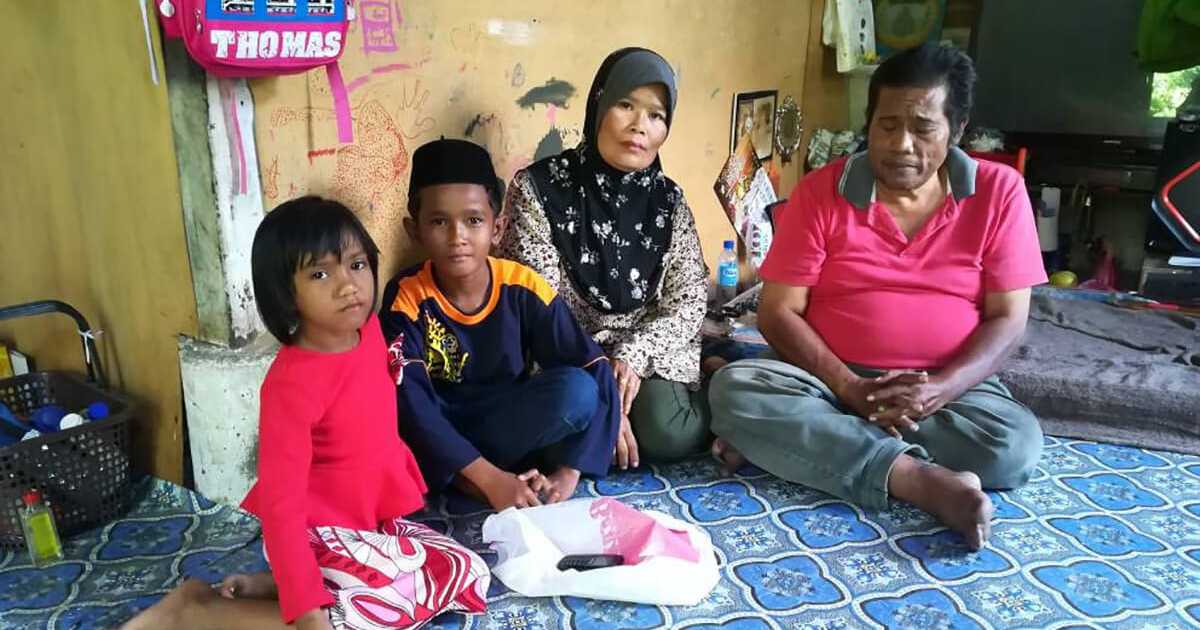


No comments for "poverty in malaysia article"
Post a Comment